Themes: Hyperacute Care, ICH, Causes
|
Martin is a 62 year old gentleman has had a moderate headache that came on at 3 pm. He was FAST positive with right sided weakness and some dysarthria and his wife called an ambulance.
Martin is on Dabigatran 150 mg BD as he has AF. He has hypertension but stopped taking his medications 1 year ago due to side effects. His BP today is now 187/100 mmHg. He has been brought in by paramedics. You attend the stroke call with the specialist nurse |
 |
|---|
1. What is the most important test
A non-contrast CT is the most important initial test. He is on Dabigatran which he took this morning and makes us more concerned that the stroke is haemorrhagic. A CT Scan is the quickest and most reliable way to determine if there is Intracerebral haemorrhage.
3. What is Dabigtran
Dabigatran is an anticoagulant (thrombin inhibitor) that helps prevent the formation of blood clots. It is one of the Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACS). It reduces the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. It can cause bleeding as a side effect.
2. A CT scan is performed.
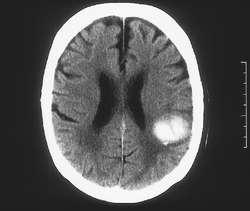
3. What does the scan show
A CT Scan confirms a haemorrhagic stroke.
His GCS is 14 and NIHSS is 12
4. What treatment is recommended
In this case he needs IV Idarucizumab (Praxbind) which is the specific antidote to Dabigatran. A formal VTE assessment should happen as the biggest risk for DVT is an old DVT. He will need IPC stockings. It is always important to do this first. Neurosurgeons would not intervene until clotting has been normalised.
5. What other treatments are given in patients with ICH who are on anticoagulants or low platelets with ICH
- Idarucizumab (Praxbind) for Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- 4 Factor Prothrombin Complex concentrate (Octplex/Beriplex) for the other DOACs
- Vitamin K + 4 Factor Prothrombin Complex concentrate (Octplex/Beriplex) for warfarin
- Platelets for significant thrombocytopenia
- Platelets are not recommended for those on antiplatelets unless significant thrombocytopenia
6. Looking at the CT what complications might occur
Bleeding into the ventricles always raises the risk of developing an obstructive hydrocephalus which would be treated with placement of an external ventricular drainage. If he was to have any further drop in GCS he would need a repeat CT and neurosurgical consult. Further and worsening haemorrhage can also occur.
7. What is (are) the cause(s) of the bleed
This looks like a hypertensive bleed which may have been worsened by being on a DOAC. We know he has a history of high BP and stopped taking his medications. The wise thing to do is to repeat an MRI/MRA at 2 months when the blood should have resolved and any persisting structural lesions can be seen.
| Note: The plan is to keep the website free through donations and advertisers that do not present any conflicts of interest. I am keen to advertise courses and conferences. If you have found the site useful or have any constructive comments please write to me at drokane (at) gmail.com. I keep a list of patrons to whom I am indebted who have contributed. If you would like to advertise a course or conference then please contact me directly for costs and to discuss a sponsored link from this site. |